Notes
HSL - the most friendly color format in CSS
CSS & Sass
3 minutes
But why?
- working with opacity is really simple, just provide the
alphavalue (0-1 or 0%-100%) - getting complimentary colors on the wheel is really simple, just subtract your hue value from 180
180deg+hueif hue is less than 180, and180deg-hueif hue is less than 180 - getting lighter/darker colors for soft backgrounds or borders or box shadows is really simple, just change the saturation or lightness. This would usually require a color function like
lighten()ordarken()in Sass. - You can get 10 different values for an entire gray scale with basic increments/decrements of 10%. Same for any other color. No need to go to Figma to get the colors or using Sass color function to do the calculation
There are two syntaxes. The modern one was introduced in 2016 and is widely supported. The other one works in IE.
1/*
2Modern syntax introduced in 2016
3space separated values
4opacity is provided to hsl() as the fourth value and can be written after a `/` separator
5
6hsl(hue saturation lightness / opacity)
7hsl(hue, saturation, lightness, opacity)
8*/
9.colorful-thing {
10 color: hsl(200deg 100% 50%);
11 border-bottom: 3px solid hsl(100deg 75% 50% / 0.2);
12}
1/*
2IE supported
3comma separated values
4opacity can only be provided with hsla()
5
6hsl(hue, saturation, lightness)
7hsla(hue, saturation, lightness, opacity)
8 */
9.colorful-thing {
10 color: hsl(200deg, 100%, 50%);
11 background-color: hsla(200deg, 100%, 50%, 0.2);
12}
HSL stands for hue, saturation, and lightness - and represents a cylindrical-coordinate representation of colors.
It helps if you imagine the color picker as a wheel instead of a slider.
hue
Defined the color pigment as a degree on the color wheel (from 0 to 3359)
- 0 (or 360) is red
- 120 is green
- 240 is blue


saturation
Defines the saturation percentage on Y-axis, deciding how vibrant the color should be
0%is completely unsaturated (gray)100%is the full color (full saturation)

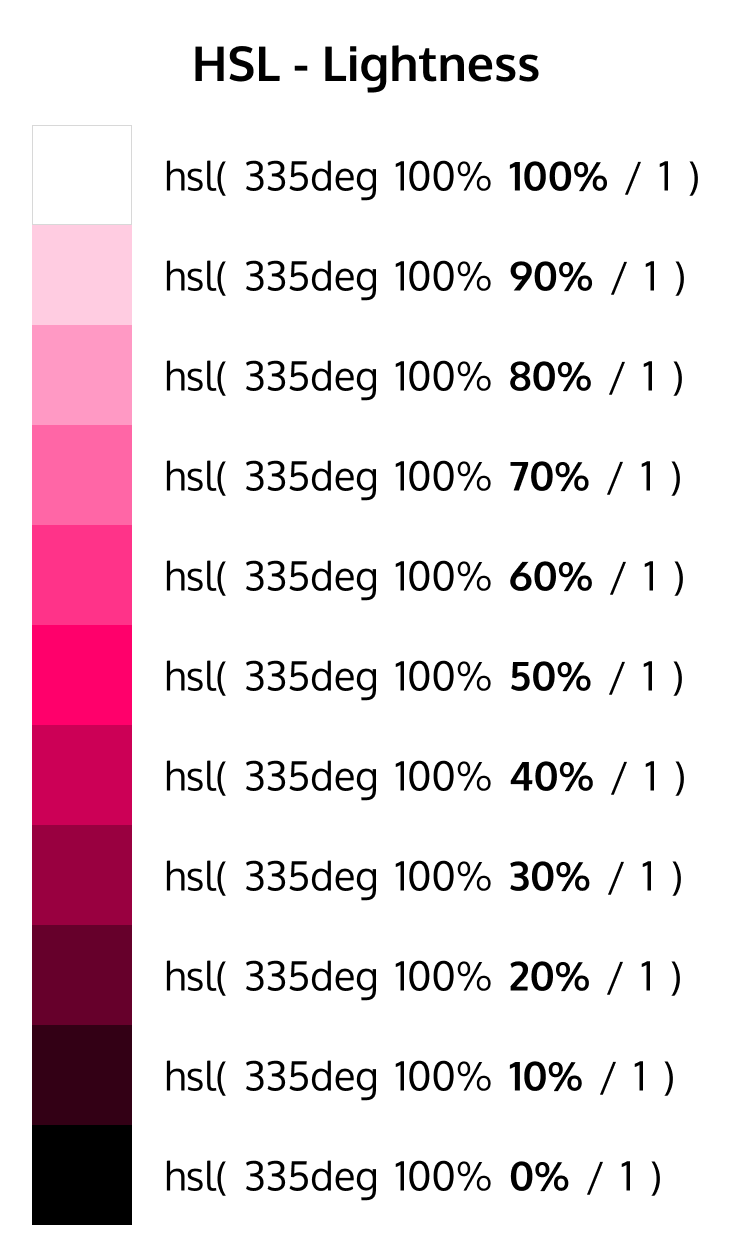
lightness
Defines the lightness percentage on X-axis, deciding how light or dark the color should be
0%is black50%is normal100%is pure white
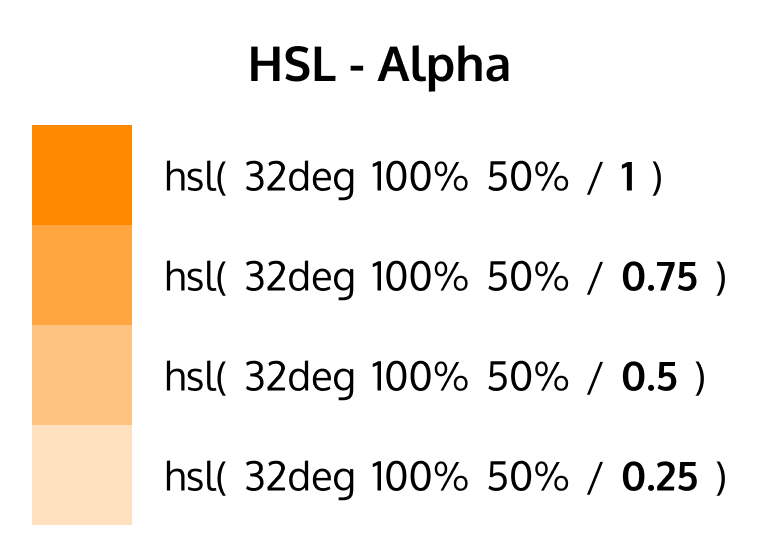
opacity
Defined the alpha value (transparency)
1or100%is fully opaque0or0%is fully transparent0.5or50%is translucent
Code sample
1<div class="first box"></div>
2<div class="second box"></div>
3<div class="third box"></div>
4<div class="fourth box"></div>
1.box {
2 width: 50px;
3 height: 50px;
4}
5
6.first.box {
7 background-color: hsl(335deg 100% 50% / 1);
8}
9.second.box {
10 background-color: hsl(335deg 100% 50% / 0.75);
11}
12.third.box {
13 background-color: hsl(335deg 100% 50% / 0.5);
14}
15.fourth.box {
16 background-color: hsl(335deg 100% 50% / 0.25);
17}
1.green { background-color:hsl(120,100%,50%); }
2.green-dark { background-color:hsl(120,100%,25%); }
3.green-light { background-color:hsl(120,100%,75%); }
4.green-pastel { background-color:hsl(120,60%,70%); }